Most people don’t spend much time looking at trees. It’s not exactly an exciting activity. Computer screens are more entertaining. Trees don’t normally go anywhere or do anything. They sway sometimes. Depending on the wind.

Most people don’t put looking at trees on their bucket list. Then again, maybe they should.
In the film “Being 97” (2020), Herbert Finagrette (1921-2018), philosopher and writer of Heavy Drinking: The Myth of Alcoholism as a Disease (1988), described looking at trees as a, “transcendent experience.”
At 97 years of age Herbert found himself looking around at the world as if he’s been asleep and saying, “Death is a frightening thought.”
No doubt others would share this sentiment, but coming from Dr. Herbert Finagrette it is somewhat ironic given that in the book Death: Philosophical Sounding (1996) Herbert argued that “there is no reason to fear death.”
Obviously, as he neared his life expectancy, things started to get real. Herbert changed his mind. “It (death) is something I don’t want to happen,” says Herbert. “Much as I think our life in this world is often a pretty messy affair, I still would like to hang around. I don’t know the basic reason why I should want to or the basic reason why I should be afraid of it.”
But then, ultimately, at 97 years of age, Herbert relaxed and found solace in trees.
“As I sit out now on my deck of the house, I look at the trees blowing in a little breeze and I’ve seen them innumerable times, but somehow, seeing the trees this time is a transcendent experience. I see how marvelous it is and I think to myself, ‘I’ve had these here all along. But have I really appreciated them‘?”
Probably not. But then, that’s probably true for most people who see trees without noticing them.
Herbert’s experience with the trees puts one in mind of that song, “What a Wonderful World“, but if someone is uninspired by this wonderful world and afraid of death, aside from looking at trees, can philosophy help?
Of course it can. Let’s begin by stepping away from lugubrious talk. Let’s walk and run with Buster while avoiding boulders and, like a philosopher, let us sing, “Ooh La La” together.
Maybe we could be more Stoic about it? The stoicism of Marcus Aurelius is popular, even today (see: The Thoughts of the Emperor Marcus Aurelius Antonius). According to Stoic philosophy the path to happiness is found by accepting the moment as it is and by not allowing yourself to be controlled by desire or fear.
And, as we all know, pretty much everything we do relates to a desire to feel good, comfortable and pain-free, but like our philosophical friend under tree-shade said, long, long ago, “Life is Dukkha.” And what is Dukkha? Dukkha is a Pali word normally translated as meaning suffering, stress or unsatisfactoriness.
Sounds about right, don’t you think? “That’s life!” as they say. You can fulfil a desire but only temporarily because in this life suffering, whether physical, emotional or mental is pretty much unavoidable.
As William de Witt Hyde (1858-1917) observed in The Five Great Philosophies of Life (1924), “gratifications are short; while appetites are long…. When a desire burns unsatisfied, the balance of our time is not pleasurable” (p. 52).
Perhaps, if thinking and acting Stoic isn’t your cup of tea (Stoics are sooo pessimistic, they always prepare for the worst!), what about Absurdism?
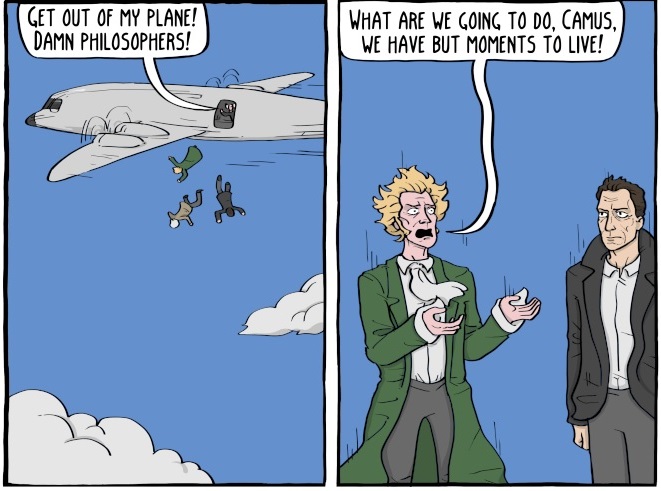
Absurdism is “the belief that human beings exist in a purposeless, chaotic universe” (dictionary). Nobel prize winning Absurdist philosopher Albert Camus (1913-1960) said (or wrote), “You will never be happy if you continue to search for what happiness consists of. You will never live if you are looking for the meaning of life!”
No doubt if Albert Camus were alive—he died at age 44 in a tragic car accident that may have been the handywork of Soviet spies, so the conspiracy goes (Britannica)—he would direct us to the myth of Sisyphus and the joy of struggle.
“The struggle itself towards the heights is enough to fill a man’s heart. One must imagine Sisyphus happy,” wrote Albert Camus who also said, “The only way to deal with an unfree world is to become so absolutely free that your very existence is an act of rebellion!”

If Absurdism isn’t your thing, because it is, after all, absurd. Maybe you could be more Epicurean about it? Whereas Stoicism focuses on how to bear pain, Epicureanism focuses on how to gain pleasure, but it isn’t just about getting all the pleasure you can or of making pain not hurt, as De Witt Hyde said, “It is a question of the worth of the things in which we find our pleasure, and the relative values of the things we suffer for” (The Five Great Philosophies of Life, p. 111).
Let’s put it together one after another with succinct advice and a graphic to illustrate:
Stoic advice: As Epictetus said in Discourses, “It is impossible for a man to learn what he thinks he already knows.” Message: Keep an open mind and heart. (There’s always more to it.)
Absurdist advice: Embrace the absurdity of life (e.g., don’t take it so serious) and find ways to navigate the world (e.g., humour) without succumbing to despair or nihilism.

Epicurean advice: “Death does not concern us, because as long as we exist, death is not here. And when it does come, we no longer exist” (Epicurus).

So, dear philosopher, with thinking, coping and practice, we can be wise.
We can save the world, our own, by being rational.
We can make the most of life by always working to make it better.
We can enjoy a chaotic and yet, beautiful ride with all those ups and downs, if we always remember and follow this simple advice, namely:
Enjoy wisely.












