Here at a Philosophy of Enjoyment there is no clickbait and shrill exclamation points are strictly avoided. Yes! Here there are no broad claims made to sell you something and no “100% Guaranteed If Not Totally Satisfied!”
With a Philosophy of Enjoyment, there are no phony directives. There is no lack of logic and no lame clichés to disenchant you. There is no, “Make All Your Dreams Come True In Three Easy Steps!” Such claims beg questioning: How do you make all your dreams come true? What if your dream is world peace and a low-cost iPhone?
What then?
That, of course, depends. It depends on your philosophy and the love you have. It depends on how you think, feel and behave. If you’re open to it and not afraid to feel silly, enjoyment can be as easy as dancing freely.
People are people. More than a few are goofy, bad and scary. Most of us start off OK—even those despised today—but then we start thinking and reacting in a negative way to a world filled with people who appear cruel, irrational and greedy.
That’s when the trouble started, back on day one.
As Hans Fallada (1893-1947) wrote in Every Man Dies Alone (1946)—later made into the movie Alone in Berlin (2017)—”This boy was three years younger than Karlemann and heading in the same way—no love, no belief, no ambition, only thinking of himself” (p. 340).
The Beatles were right all along: “All You Need Is Love“.
Love is not just the domain of religion. Look at what religious people do! It’s like every self is one and the same, and differences, a matter of opinion. Anyone can be duped by fear, hate or desire, but of course, everyone knows that, don’t they?
It’s a matter of understanding.
Clickbait is prone to hyperbole, as in, a claim that’s “not meant to be taken literally, but used to create dramatic effect” (Seneca Learning).

Exaggeration is used to stir desire so you’ll buy what’s being pitched (10% off if you buy four). Getting you to want something is the sole purpose of advertising and propaganda (not to be confused with soul purpose which is quite different).
From the word hyperbole we get the word hyperbolic which is an “exaggerated claim,” that is, unless you’re talking hyperbolic geometry. Exaggerated claims tend to be short-sighted, superficial, misleading, and more than probably, disappointing—especially if you do what’s advised and no dreams are forthcoming.
It’s disappointing when expectations are thwarted by realities beyond our control.
We swim in a world where advertisers and propagandists tell us who we are, what we should be, and what values to share.
Advertising executive Jonas Sachs said this about ads, “We see 3,500 of them a day and the majority of them basically tell us you suck and if you don’t buy this product, you’re not going to be rich enough, smart enough, hot enough, and so we walk around being told 3,500 times a day how deficient and lame we are” (How Commercials Get Us to Buy Crap We Don’t Need).
No wonder people get depressed.

If you watch the News or get caught in the crossfire, it’s even more depressing. There are maniacs in politics who are greedy, hateful and fear-filled who get others who are greedy, hateful and fearful to do their bidding. Without checks and balances, anyone can run amuck for self-focused reasons.
And therein is the problem: Who is this self causing all the problems?
As our natural environment gets trashed for reasons of comfort, convenience and violence, supposedly good people who claim to love others, go ahead and kill and elbow those in their way.
Silly humans. They rage and fight and trash others with words, fists and guns (sometimes with knives).
As nutty old Nietzsche observed in Thus Spake Zarathustra (1883), “You yourself are the worst enemy you can encounter” (Freedom in Thought). This holds true for everybody: good, bad and nutty (including Nietzsche).
Consider your Philosophy of Enjoyment as a way to get away from not enjoying. No need to buy, do, or go anywhere. First, become aware of how one is manipulated by one’s self and others and then: Do nothing. Think, “Nothing is going to bring me down“.
With a Philosophy of Enjoyment we listen to thoughts and feelings like they’re messengers. We don’t deny them. We accept the flow of passing thoughts and feelings and ground our behaviour in reality like the psychiatrist Dr. Shoma Morita (1874-1938) recommended.
The goal is to not let one’s ego or “I think” or “I want” or “I feel” run the show. The problem of unhappiness isn’t a matter of alleviating discomfort by ignoring thoughts and feelings. Thoughts and feelings cause problems when not addressed directly. To take action in one’s life is to not be ruled by passing fancies (Morita therapy: 1919 to 1995).
Here with yours truly, with consideration, humour, an open mind and accepting nature, by experimenting with what’s recommended, you can find advice that could change your life—even if that advice is unsolicited.
The goal is to use one’s way of thinking and feeling to understand what’s happening. Through a Philosophy of Enjoyment anyone can avoid conflict to experience beauty, forgiveness and an over-abiding feeling of happiness no matter what the situation.
Happiness comes from our being alive, not from a bag, bottle, needle or store. The goal of it all is to experience a peace of mind which can’t be bought and paid for with any amount of money.
In this philosophy we consider nuance and complexity. A person’s feelings and thoughts tend to exaggerate either the negative or positive consequences of a now-threat (the Russians are coming) or a now-reward (shark fin soup makes me happy).
The primary role of one’s brain is to help one navigate the environment. Threats and rewards fire in different parts of the brain. On a basic level our brains avoid threats and seek reward, “Cortisol makes us see things in black or white, yes or no and leads us to over-assess the level of threat in front of us. From an evolutionary viewpoint, those ancestors that thought “better safe than sorry” presumably lasted a little bit longer” (Threat vs Reward).
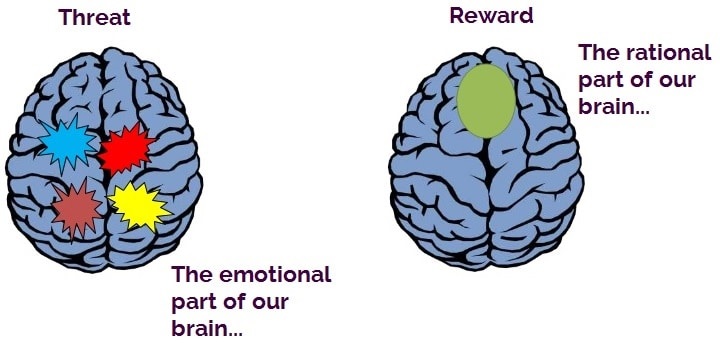
In the old days before hairdryers, Artificial Intelligence, missiles and fingernail clippers, this orientation was useful for finding food and avoiding being eaten, but in the 21st century, it creates problems.
And there it is. Watch what you think and feel and don’t do anything to add inflammation. Take the high road. As Dr. Morita said, “Accept your feelings. Know your purpose. And do what needs to be done.” And, when it’s safe, we can dance. And, if you don’t dance, you can enjoy a good song.
On behalf of life, life is all we have. Why not enjoy it?